Report on Piton de la Fournaise (France) — September 1998
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 23, no. 9 (September 1998)
Managing Editor: Richard Wunderman.
Piton de la Fournaise (France) Activity ends with fissure eruptions outside the caldera
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 1998. Report on Piton de la Fournaise (France) (Wunderman, R., ed.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 23:9. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN199809-233020
Piton de la Fournaise
France
21.244°S, 55.708°E; summit elev. 2632 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
The eruption that began in March (BGVN 23:03) diminished during August and September. Observatoire Volcanologique du Piton de la Fournaise (OVPF) considers the eruption ended. The most significant activity during the last two months took place outside the caldera.
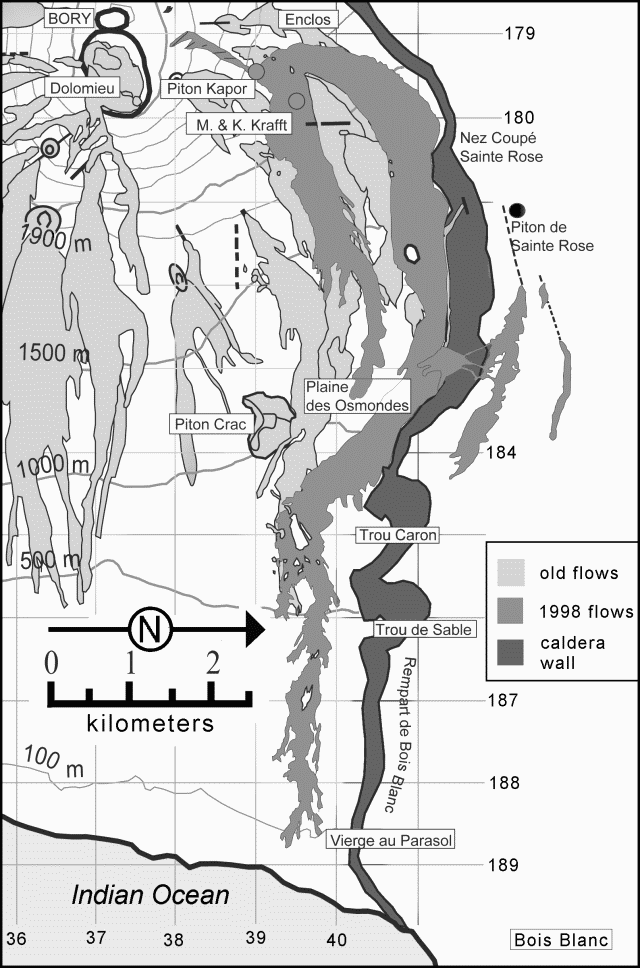
A small fissure eruption began on 9 August north of the caldera. Lava issued from this fissure, which was located ~500 m from the caldera wall near Nez Coupé Sainte Rose (figure 49). The initial eruption lasted only 24 hours, but a second fissure eruption began 14 August in the same area closer to the caldera wall. No fountains were observed with the second fissure, although the lava was very fluid. Flows eventually measured 200-300 m wide and ~2 km long. They moved parallel to the caldera wall until 14 September when they stopped ~500 m above Trou Caron. Some of the lava reached the edge of the caldera and spilled over onto the Plaine des Osmondes through three separate rivulets. A flow that was moving towards the upper part of Bois Blanc (a village located on the east coast) stopped by 25 August.
During September, some night incandescence due to the lava lake at Piton Kapor was seen. Only weak tremor was observed. Beginning 5 September some gas-piston events were recorded; these had likely taken place before, but had remained undetected during stronger episodes of tremor.
This eruption, including all tremor and degassing at Piton Kapor, ended 21 September, after 196 days of activity. It thus comprised the volcano's longest and one of it's most voluminous eruptions of this century.
Geological Summary. Piton de la Fournaise is a massive basaltic shield volcano on the French island of Réunion in the western Indian Ocean. Much of its more than 530,000-year history overlapped with eruptions of the deeply dissected Piton des Neiges shield volcano to the NW. Three scarps formed at about 250,000, 65,000, and less than 5,000 years ago by progressive eastward slumping, leaving caldera-sized embayments open to the E and SE. Numerous pyroclastic cones are present on the floor of the scarps and their outer flanks. Most recorded eruptions have originated from the summit and flanks of Dolomieu, a 400-m-high lava shield that has grown within the youngest scarp, which is about 9 km wide and about 13 km from the western wall to the ocean on the E side. More than 150 eruptions, most of which have produced fluid basaltic lava flows, have occurred since the 17th century. Only six eruptions, in 1708, 1774, 1776, 1800, 1977, and 1986, have originated from fissures outside the scarps.
Information Contacts: Thomas Staudacher, Observatoire Volcanologique du Piton de la Fournaise (OVPF), 14 RN3, le 27Km, 97418 La Plaine des Cafres, La Réunion, France.