Report on Stromboli (Italy) — September 2020
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 45, no. 9 (September 2020)
Managing Editor: Edward Venzke.
Edited by Kadie L. Bennis.
Stromboli (Italy) Strombolian activity continues at both summit craters during May-August 2020
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2020. Report on Stromboli (Italy) (Bennis, K.L., and Venzke, E., eds.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 45:9. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN202009-211040
Stromboli
Italy
38.789°N, 15.213°E; summit elev. 924 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
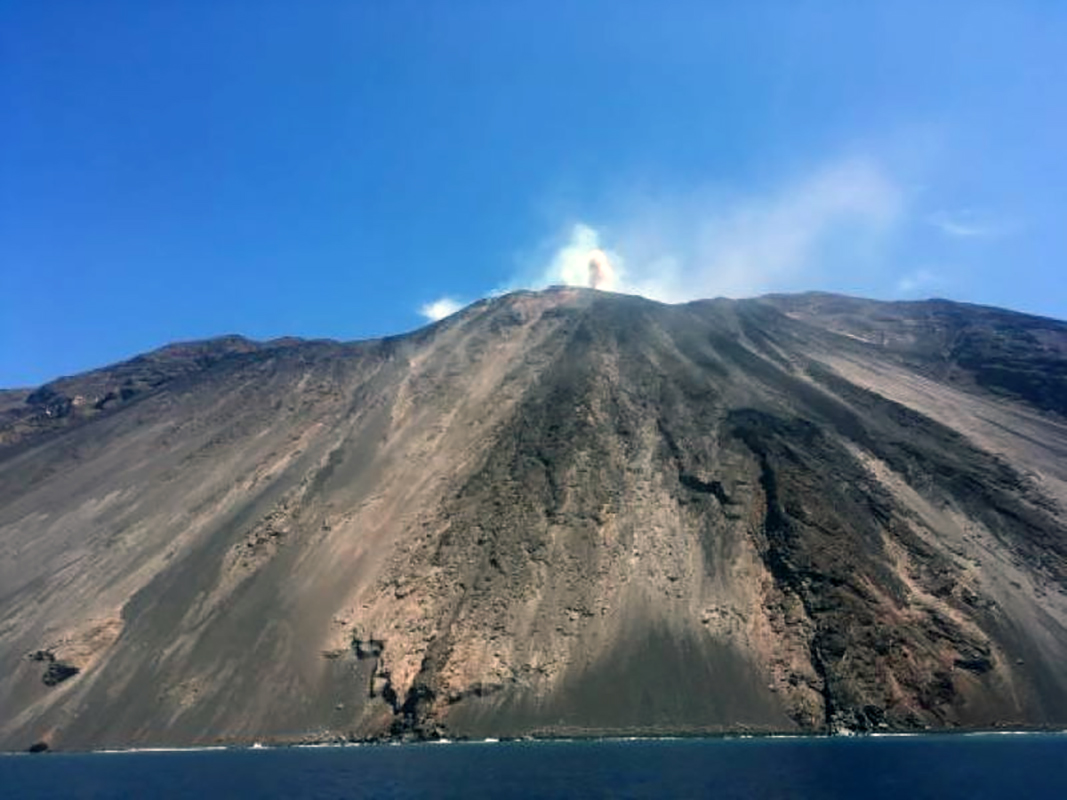
Stromboli, located in northeastern-most part of the Aeolian Islands, is composed of two active summit vents: the Northern (N) Crater and the Central-South (CS) Crater that are situated at the head of the Sciara del Fuoco, a large scarp that runs from the summit down the NW side of the volcano. The current eruption period began in 1934, continuing to the present with volcanism characterized by consistent Strombolian explosions in both summit craters, ash plumes, pyroclastic flows, and occasional lava flows (BGVN 45:08). This report updates activity consisting of dominantly Strombolian explosions and ash plumes from May to August 2020 with information primarily from daily and weekly reports by Italy's Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV) and various satellite data.
Activity was consistent during this reporting period. Explosion rates ranged from 1-23 events per hour and were of variable intensity, producing material that typically rose from less than 80 to over 300 m above the crater. One ash plume on 19 July rose 1 km above the crater and high energy ballistics were ejected 500 m above the crater during the week of 20-26 July (table 9). Strombolian explosions were often accompanied by gas-and-steam emissions and spattering that has occasionally resulted in material deposited on the slopes of the Sciara del Fuoco. According to INGV, the average SO2 emissions measured 250-300 tons/day.
Table 9. Summary of activity at Stromboli during May-August 2020. Low-intensity activity indicates ejecta rising less than 80 m, medium-intensity is ejecta rising less than 150 m, and high-intensity is ejecta rising over 200 m above the vent. Data courtesy of INGV.
| Month | Activity |
| May 2020 | Strombolian activity and degassing continued with some spattering. Explosion rates varied from 1-17 per hour. Ejected material rose 80-150 m above the N crater and 150-250 m above the CS crater. The average SO2 emissions measured 300 tons/day. |
| Jun 2020 | Strombolian activity and degassing continued with spattering. Explosion rates varied from 2-14 per hour. Ejected material rose 80-200 m above the N crater and 150 m above the CS crater. Spattering was primarily focused in the CS crater. The average SO2 emissions measured 300 tons/day. |
| Jul 2020 | Strombolian activity and degassing continued with some spattering. Explosion rates varied from 1-12 per hour. Ejected material rose 80-1,000 m above the N crater. Spattering was primarily focused in the CS crater. The average SO2 emissions measured 300 tons/day. |
| Aug 2020 | Strombolian activity continued with discontinuous spattering. Explosion rates varied from 1-23 per hour. Ejected material rose at least 200 m above the N crater and at least 250 m above the CS crater. |
Explosive activity was relatively consistent during May 2020 and was mainly produced in 3-4 eruptive vents in the N crater and at least two eruptive vents in the CS crater. As a result of some explosions fallout covered the slopes of the Sciara del Fuoco. Explosion rates varied from 1-17 per hour in the N crater and 1-8 per hour in the CS crater; ejected material rose 80-250 m above the craters.
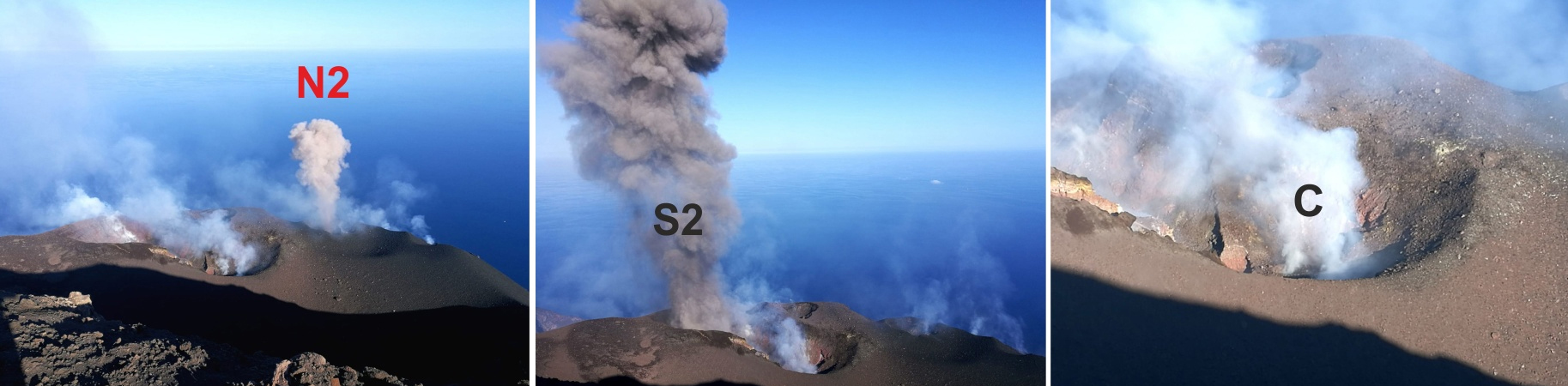
During June, explosions originated from 2-3 eruptive vents in the N crater and at least 2-3 localized vents in the CS crater. The Strombolian explosions ejected material 80-200 m above the craters, some of which fell back onto the Sciara (figure 182). Explosion rates varied from 5-14 per hour in the N crater and 2-9 per hour in the CS crater. Spattering was typically observed in the CS crater.
Ongoing explosive activity continued into July, originating from 2-3 eruptive vents in the N crater and 3-4 eruptive vents in the CS crater. Explosions varied from 3-12 per hour in the N crater and 1-11 per hour in the CS crater; ejected lapilli and bombs rose 80-1,000 m above the craters (figure 183). On 19 July a high-energy explosion between 0500 and 0504 produced an ash plume containing ejecta more than 50 cm that rose to a maximum of 1 km above the crater, with fallout reaching the Pizzo sopra la Fossa and resulting in ashfall on the Sciara and the towns of Liscione and Roccette. During the week of 20-26 July explosions in the E portion of the volcano ejected ballistics 500 m above the crater; the size and shape of these varied between slag bombs to clasts greater than 50 cm.
Strombolian activity accompanied by discontinuous spattering continued during August. Total daily explosions varied from 3-23 per hour ejecting material that up to 200-250 m above the craters. During the first half of the month the explosions were low-intensity and consisted of fine material. On 13 August the intensity of the explosions increased, producing an ash plume that rose 300 m above the crater drifting SE and resulting in a significant amount of ashfall on the Sciara. During the week of 17-23, explosions in the N1 crater ejected material 200 m above the crater while explosions in the CS crater ejected material 250 m above the crater, predominantly during 22 August in the S2 crater (figure 184).
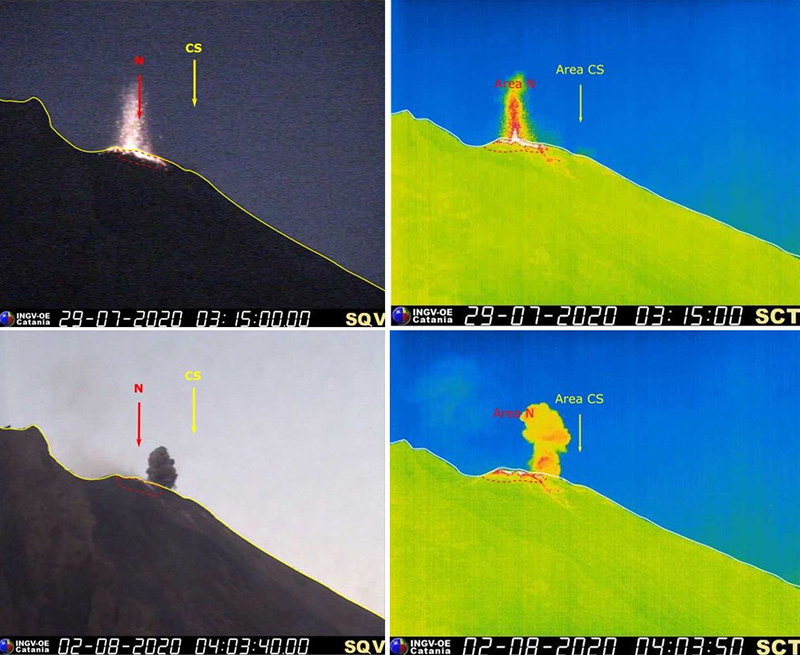
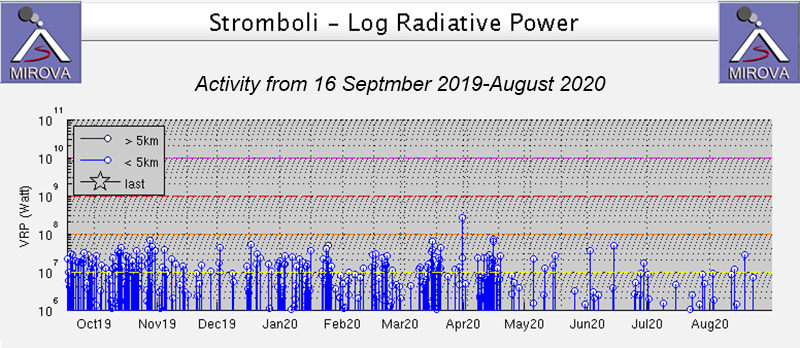
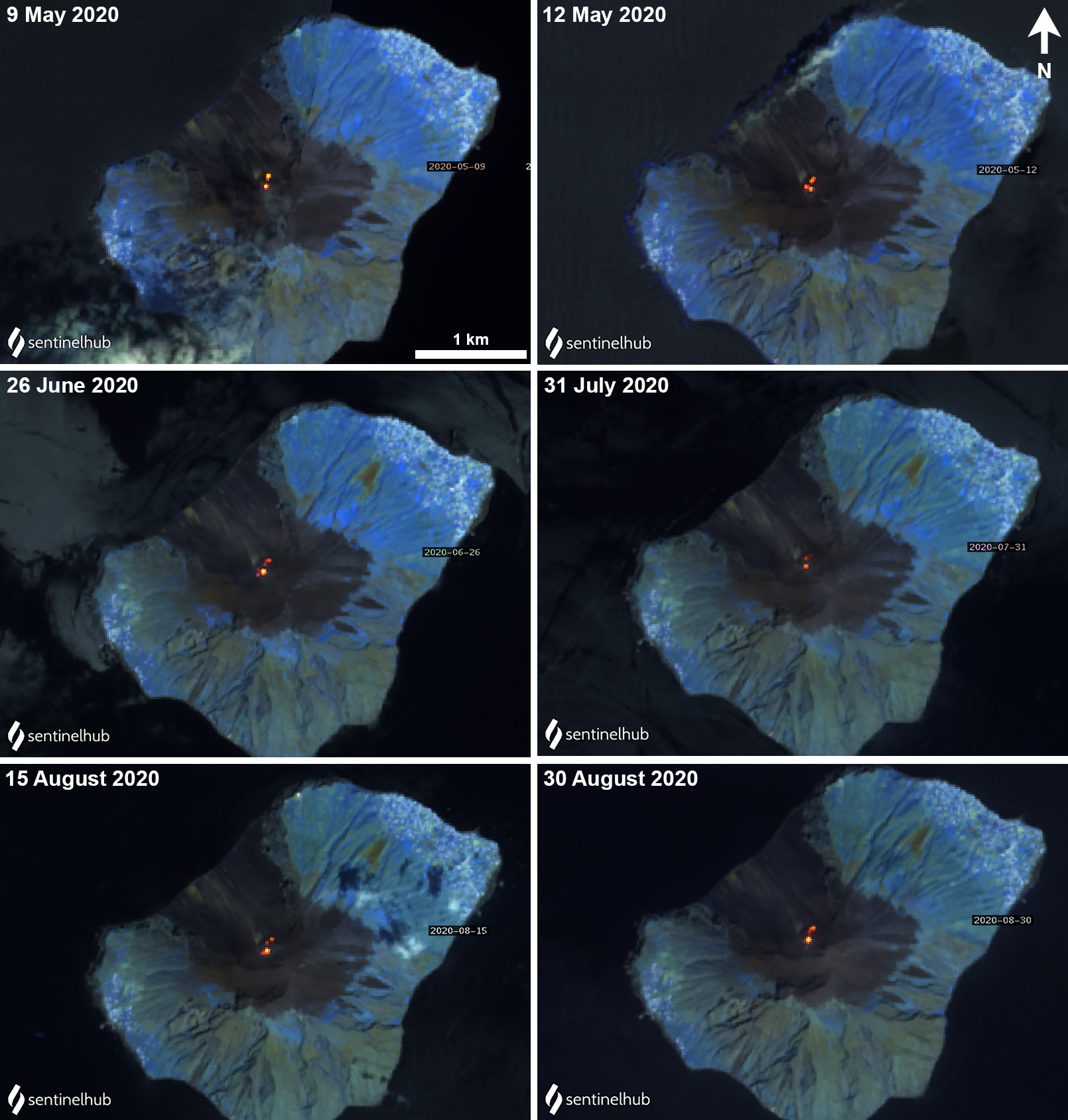
Moderate thermal activity was relatively consistent from October 2019 through mid-April 2020; during May-August thermal activity became less frequent and anomalies were lower in power based on the MIROVA Log Radiative Power graph using MODIS infrared satellite information (figure 185). Though there were no detected MODVOLC thermal alerts during this reporting period, many thermal hotspots were observed in Sentinel-2 thermal satellite imagery in both summit craters (figure 186).
Geological Summary. Spectacular incandescent nighttime explosions at Stromboli have long attracted visitors to the "Lighthouse of the Mediterranean" in the NE Aeolian Islands. This volcano has lent its name to the frequent mild explosive activity that has characterized its eruptions throughout much of historical time. The small island is the emergent summit of a volcano that grew in two main eruptive cycles, the last of which formed the western portion of the island. The Neostromboli eruptive period took place between about 13,000 and 5,000 years ago. The active summit vents are located at the head of the Sciara del Fuoco, a prominent scarp that formed about 5,000 years ago due to a series of slope failures which extends to below sea level. The modern volcano has been constructed within this scarp, which funnels pyroclastic ejecta and lava flows to the NW. Essentially continuous mild Strombolian explosions, sometimes accompanied by lava flows, have been recorded for more than a millennium.
Information Contacts: Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV), Sezione di Catania, Piazza Roma 2, 95123 Catania, Italy, (URL: http://www.ct.ingv.it/en/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground).