Report on Ebeko (Russia) — December 2020
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 45, no. 12 (December 2020)
Managing Editor: Edward Venzke.
Edited by Kadie L. Bennis.
Ebeko (Russia) Continued explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall; June-November 2020
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2020. Report on Ebeko (Russia) (Bennis, K.L., and Venzke, E., eds.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 45:12. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN202012-290380
Ebeko
Russia
50.686°N, 156.014°E; summit elev. 1103 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Volcanism at Ebeko, located on the N end of the Paramushir Island in the Kuril Islands, has been ongoing since October 2016, characterized by frequent moderate explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall in Severo-Kurilsk (7 km ESE) (BGVN 45:05). Similar activity during this reporting period of June through November 2020 continues, consisting of frequent explosions, dense ash plumes, and occasional ashfall. Information for this report primarily comes from the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) and satellite data.
Activity during June was characterized by frequent, almost daily explosions and ash plumes that rose to 1.6-4.6 km altitude and drifted in various directions, according to KVERT reports and information from the Tokyo VAAC advisories using HIMAWARI-8 satellite imagery and KBGS (Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service) seismic data. Satellite imagery showed persistent thermal anomalies over the summit crater. On 1 June explosions generated an ash plume up to 4.5 km altitude drifting E and S, in addition to several smaller ash plumes that rose to 2.3-3 km altitude drifting E, NW, and NE, according to KVERT VONA notices. Explosions on 11 June generated an ash plume that rose 2.6 km altitude and drifted as far as 85 km N and NW. Explosions continued during 21-30 June, producing ash plumes that rose 2-4 km altitude, drifting up to 5 km in different directions (figure 26); many of these eruptive events were accompanied by thermal anomalies that were observed in satellite imagery.
 |
Figure 26. Photo of a dense gray ash plume rising from Ebeko on 22 June 2020. Photo by L. Kotenko (color corrected), courtesy of IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
Explosions continued in July, producing ash plumes rising 2-5.2 km altitude and drifting for 3-30 km in different directions. On 3, 6, 15 July explosions generated an ash plume that rose 3-4 km altitude that drifted N, NE, and SE, resulting in ashfall in Severo-Kurilsk. According to a Tokyo VAAC advisory, an eruption on 4 July produced an ash plume that rose up to 5.2 km altitude drifting S. On 22 July explosions produced an ash cloud measuring 11 x 13 km in size and that rose to 3 km altitude drifting 30 km SE. Frequent thermal anomalies were identified in satellite imagery accompanying these explosions.
In August, explosions persisted with ash plumes rising 1.7-4 km altitude drifting for 3-10 km in multiple directions. Intermittent thermal anomalies were detected in satellite imagery, according to KVERT. On 9 and 22 August explosions sent ash up to 2.5-3 km altitude drifting W, S, E, and SE, resulting in ashfall in Severo-Kurilsk. Moderate gas-and-steam activity was reported occasionally during the month.
Almost daily explosions in September generated dense ash plumes that rose 1.5-4.3 km altitude and drifted 3-5 km in different directions. Moderate gas-and-steam emissions were often accompanied by thermal anomalies visible in satellite imagery. During 14-15 September explosions sent ash plumes up to 2.5-3 km altitude drifting SE and NE, resulting in ashfall in Severo-Kurilsk. On 22 September a dense gray ash plume rose to 3 km altitude and drifted S. The ash plume on 26 September was at 3.5 km altitude and drifted SE (figure 27).
 |
Figure 27. Photos of dense ash plumes rising from Ebeko on 22 (left) and 26 (right) September 2020. Photos by S. Lakomov (color corrected), IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
During October, near-daily ash explosions continued, rising 1.7-4 km altitude drifting in many directions. Intermittent thermal anomalies were identified in satellite imagery. During 7-8, 9-10, and 20-22 October ashfall was reported in Severo-Kurilsk.
Explosions in November produced dense gray ash plumes that rose to 1.5-5.2 km altitude and drifted as far as 5-10 km, mainly NE, SE, E, SW, and ENE. According to KVERT, thermal anomalies were visible in satellite imagery throughout the month. On clear weather days on 8 and 11 November Sentinel-2 satellite imagery showed ashfall deposits SE of the summit crater from recent activity (figure 28). During 15-17 November explosions sent ash up to 3.5 km altitude drifting NE, E, and SE which resulted in ashfall in Severo-Kurilsk on 17 November. Similar ashfall was observed on 22-24 and 28 November due to ash rising to 1.8-3 km altitude (figure 29). Explosions on 29 November sent an ash plume up to 4.5 km altitude drifting E (figure 29). A Tokyo VAAC advisory reported that an ash plume drifting SSE on 30 November reached an altitude of 3-5.2 km.
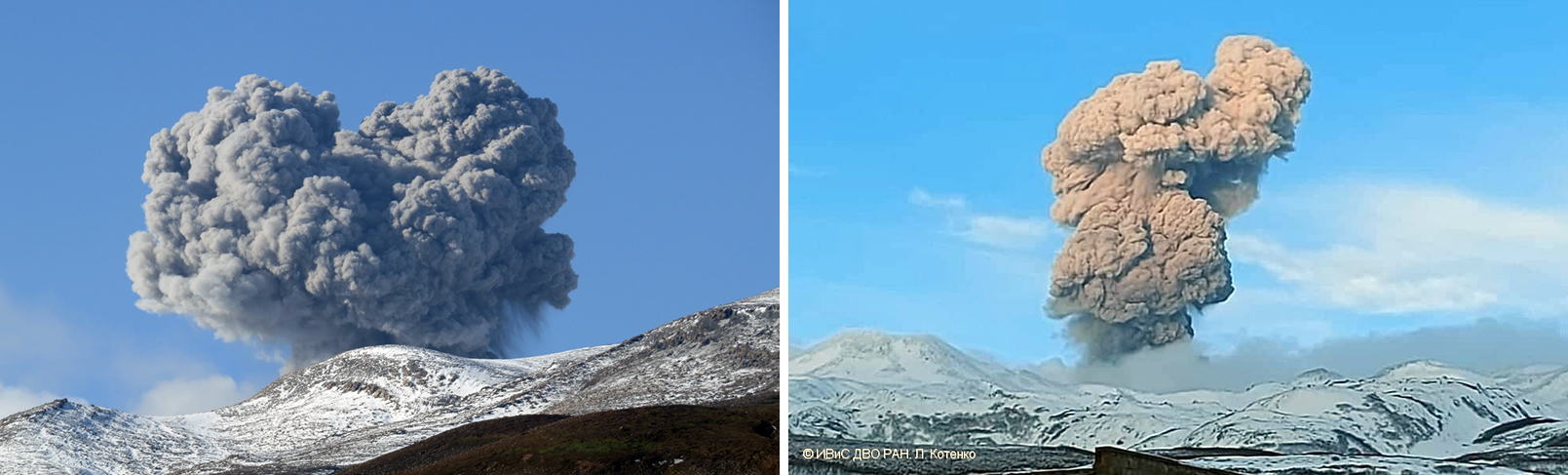 |
Figure 29. Photos of continued ash explosions from Ebeko on 28 October (left) and 29 November (right) 2020. Photos by S. Lakomov (left) and L. Kotenko (right), courtesy of IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
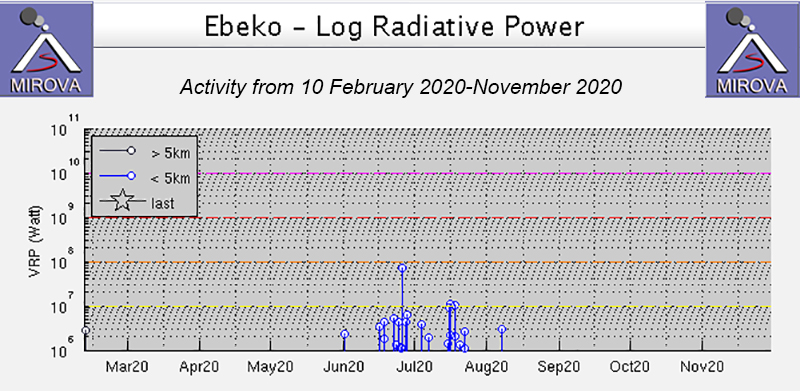
MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) analysis of MODIS satellite data shows a pulse in low-power thermal activity beginning in early June through early August (figure 30). On clear weather days, the thermal anomalies in the summit crater are observed in Sentinel-2 thermal satellite imagery, accompanied by occasional white-gray ash plumes (figure 31). Additionally, the MODVOLC algorithm detected a single thermal anomaly on 26 June.
Geological Summary. The flat-topped summit of the central cone of Ebeko volcano, one of the most active in the Kuril Islands, occupies the northern end of Paramushir Island. Three summit craters located along a SSW-NNE line form Ebeko volcano proper, at the northern end of a complex of five volcanic cones. Blocky lava flows extend west from Ebeko and SE from the neighboring Nezametnyi cone. The eastern part of the southern crater contains strong solfataras and a large boiling spring. The central crater is filled by a lake about 20 m deep whose shores are lined with steaming solfataras; the northern crater lies across a narrow, low barrier from the central crater and contains a small, cold crescentic lake. Historical activity, recorded since the late-18th century, has been restricted to small-to-moderate explosive eruptions from the summit craters. Intense fumarolic activity occurs in the summit craters, on the outer flanks of the cone, and in lateral explosion craters.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service, Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS) (URL: http://www.emsd.ru/); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground).