Report on Aira (Japan) — July 2023
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 48, no. 7 (July 2023)
Managing Editor: Benjamin Andrews.
Edited by Kadie L. Bennis.
Aira (Japan) Intermittent explosions, eruption plumes, and ashfall during January-June 2023
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2023. Report on Aira (Japan) (Bennis, K.L., and Andrews, B., eds.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 48:7. Smithsonian Institution.
Aira
Japan
31.5772°N, 130.6589°E; summit elev. 1117 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Aira caldera, located in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay, contains the active post-caldera Sakurajima volcano near the southern tip of Japan’s Kyushu Island. Eruptions date back to the 8th century and have deposited ash on Kagoshima, one of Kyushu’s largest cities, 10 km W from the summit. The Minamidake summit cone and crater has had persistent activity since 1955; the Showa crater on the E flank has also been intermittently active since 2006. The current eruption period began during late March 2017 and has more recently consisted of explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall (BGVN 48:01). This report covers activity during January through June 2023, characterized by intermittent explosions, eruption events, eruption plumes, and ashfall from both summit craters, according to monthly activity reports from the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and satellite data.
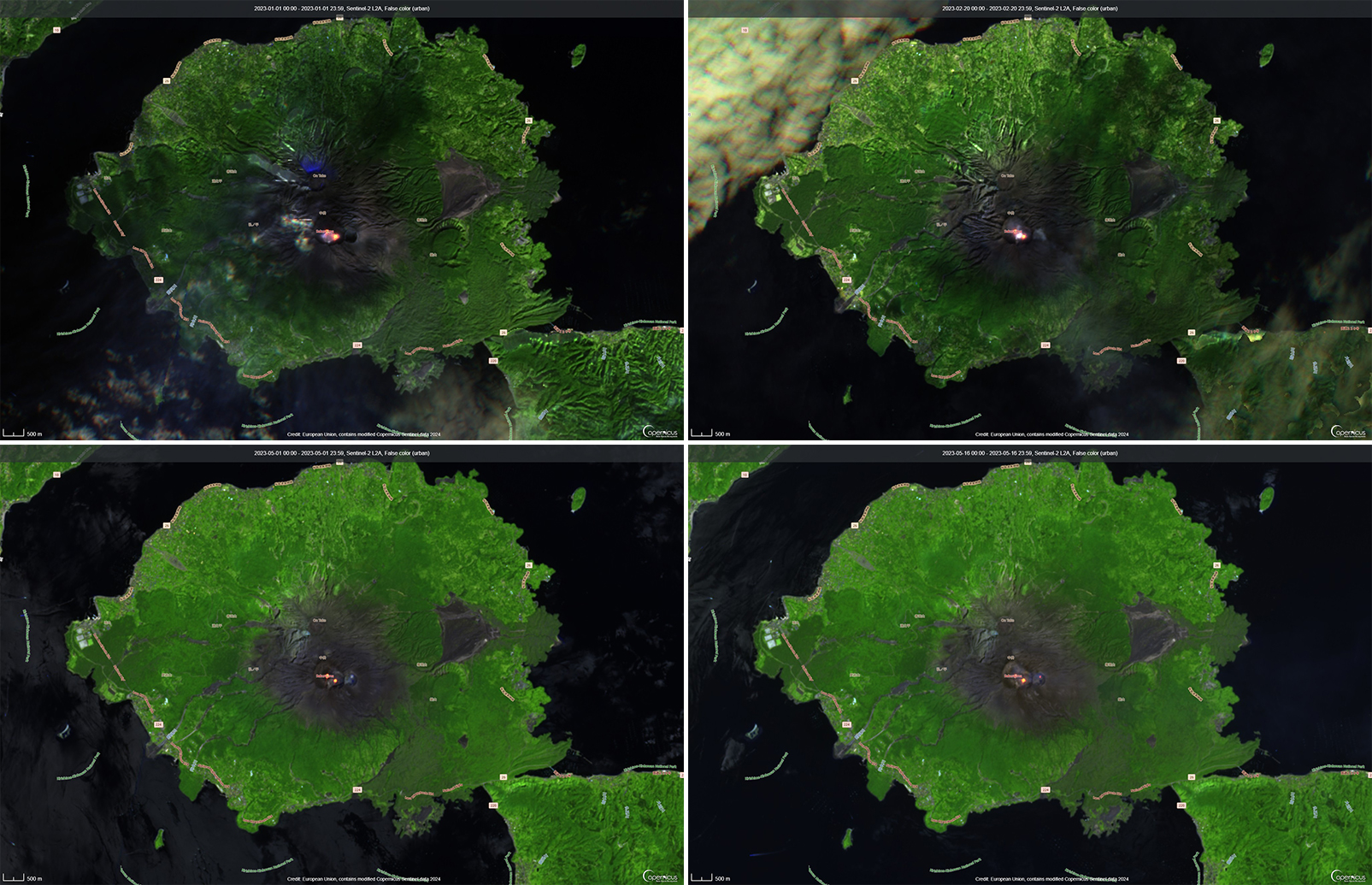
Thermal activity remained at low levels during this reporting period; less than ten thermal anomalies were detected each month by the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) system (figure 139). Occasional thermal anomalies were visible in infrared satellite images mainly at the Minamidake crater (Vent A is located to the left and Vent B is located to the right) and during May, in the Showa crater on the E flank (figure 140).
Table 29. Number of monthly explosive events, days of ashfall, area of ash covered, and sulfur dioxide emissions from Sakurajima’s Minamidake crater at Aira during January-June 2023. Note that smaller ash events are not listed. Ashfall days were measured at Kagoshima Local Meteorological Observatory, and ashfall amounts represent material covering all the Kagoshima Prefecture. Data courtesy of JMA monthly reports.
| Month | Explosive events | Days of ashfall | Ashfall amount (g/m3) | SO2 emissions (tons/day) |
| Jan 2023 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 1,000-2,800 |
| Feb 2023 | 11 | 7 | 6 | 1,900-3,500 |
| Mar 2023 | 8 | 6 | 9 | 2,100-3,500 |
| Apr 2023 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1,800-2,700 |
| May 2023 | 10 | 13 | 10 | 1,800-3,900 |
| Jun 2023 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 1,400-1,900 |
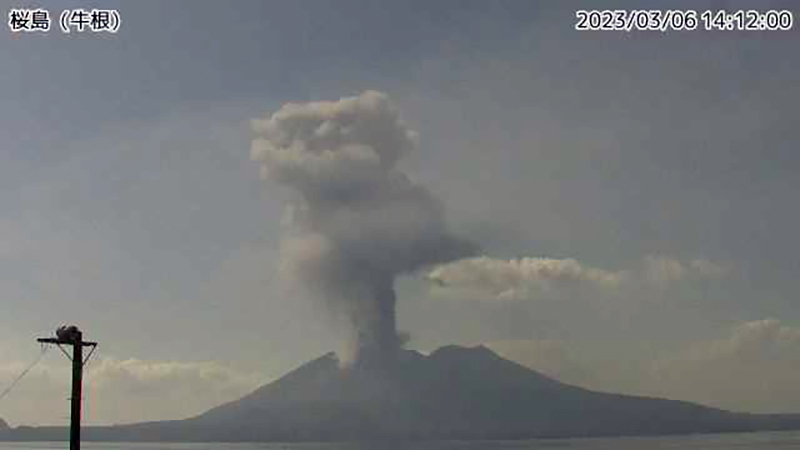
JMA reported that during January 2023, there were 14 eruptions, nine of which were explosion events. Accompanying eruption plumes rose 2.4 km above the crater rim. Large blocks were ejected 800-1,100 m from the Minamidake crater. Nighttime incandescence was observed in the Minamidake crater using a high-sensitivity surveillance camera. No eruptions in the Showa crater were reported, though there was a gradual increase in the amount of white gas-and-steam emissions beginning around mid-January. Seismicity consisted of 121 volcanic earthquakes, which was higher than the 78 earthquakes in December. The Kagoshima Local Meteorological Observatory reported a total of 2 g/m2 of ashfall was observed over the course of two days of the month. According to field surveys, daily sulfur dioxide emissions ranged from 1,000-2,800 tons/day (t/d); emissions have remained at comparable, elevated, levels since July 2022. Explosions were reported on 3 January at 1615, 8 January at 0642 and 1955, 18 January at 1215, 19 January at 0659, 21 January at 0307, and 28 January at 2342 where eruption plumes rose 1-2.4 km above the Minamidake crater and drifted SE and S. The explosion at 0307 on 21 January generated an eruption plume 1.6 km above the crater rim and ejected large blocks 800-1,100 m from the crater rim; crater incandescence was also visible (figure 141). On 28 January at 2342 an explosion produced an eruption plume that rose 2-2.2 km above the Minamidake summit crater and drifted SE.
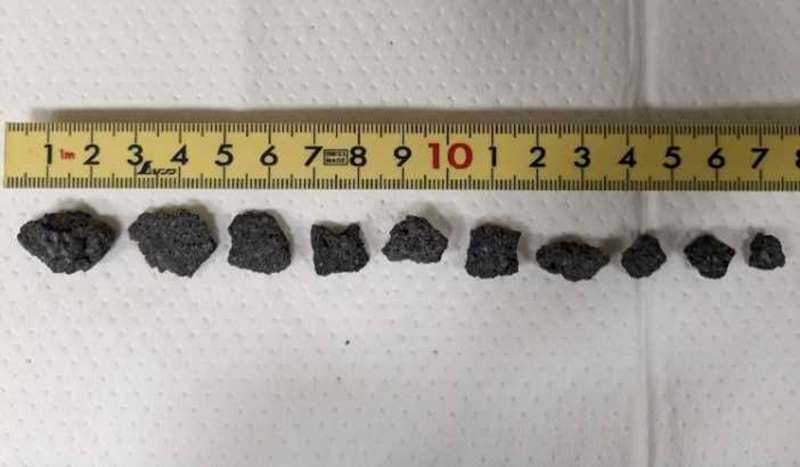
There were 26 eruptions reported during February, 11 of which were explosion events. Eruption plumes rose 2.4 km above the crater rim. Large blocks were ejected 800-1,100 m from the Minamidake summit crater, and daily nighttime crater incandescence continued. Occasional eruptive activity was observed in the Showa crater starting on 8 February, which included four eruptions (figure 142). The last time activity was reported in the Showa crater was early April 2018, according to JMA. There were 130 volcanic earthquakes detected during the month. Sulfur dioxide emissions ranged from 1,900-3,500 t/d. On 8 February large blocks were ejected 300-500 m from the Showa crater and an accompanying eruption plume rose 1.5 km above the crater rim. Summit crater incandescence was also visible at night during 8 and 21-26 February at the Showa crater. Weak crater incandescence was also reported on 8 February at the Minamidake summit crater. Explosions were recorded at 1815 on 9 February, at 1007 on 11 February, at 1448 on 14 February, at 0851 on 16 February, at 0206 on 19 February, at 2025 on 20 February, at 0937 and at 1322 on 21 February, and at 0558 on 28 February. Volcanic plumes rose 300-2,000 m above the Minamidake crater and drifted N, E, S, SE, and NE. An explosion at 1448 on 14 February at the Minamidake summit crater ejected large blocks 800-1,100 m from the crater. The eruption plume rose 800-1,200 m above the crater and drifted S. A field survey conducted on 14 February showed that the ejected volcanic clasts measured up to 3 cm in diameter, though most were smaller in size, and were deposited in Arimura, Kagoshima City (3 km SE) (figure 143). An aerial survey conducted by the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force Air Group (JMSDF) on 21 February confirmed white gas-and-steam plumes rising from the N side of the Showa crater and water was visible at the bottom of the crater. Ashfall measurements showed that a total of 6 g/m2 fell over seven days during the month at the Kagoshima Local Metrological Observatory.
During March, 22 eruptions were reported, eight of which were explosion events. Volcanic plumes rose 2.8 km above the crater rim. There were four eruptions recorded at the Showa crater, for a total of eight eruptions during February and March. Large volcanic blocks were ejected 1,000-1,300 m from the Minamidake crater and nighttime incandescence remained visible at night, based on webcam images. Blocks ejected from the Showa crater traveled 500-800 m and accompanying eruption plumes rose 2.7 km above the crater rim. Nighttime crater incandescence was reported during 4-5 March at the Showa crater, based on webcam images. Seismicity included 97 volcanic earthquakes detected throughout the month. According to the Kagoshima Local Meteorological Observatory, a total of 9 g/m2 ashfall was observed over six days of the month. A field survey reported that 2,100-3,500 t/d of sulfur dioxide was released during the month. An eruption was detected at the Showa crater at 1404 on 6 March, that ejected blocks 500-800 m from the crater, accompanied by an eruption plume that rose 2.7 km above the crater rim (figure 144). Explosions were detected at 0116 on 3 March, at 2157 on 4 March, at 1322 on 8 March, at 2228 on 11 March, at 0418 on 14 March, and at 0035 on 22 March. Eruption plumes rose 1-2.8 km above the Minamidake crater and drifted SE, NE, NW, S, and SW. At 0035 on 22 March an explosion generated an eruption plume that rose 1.2 km above the Minamidake crater and drifted SW. Material was ejected 1-1.3 km from the Minamidake crater.
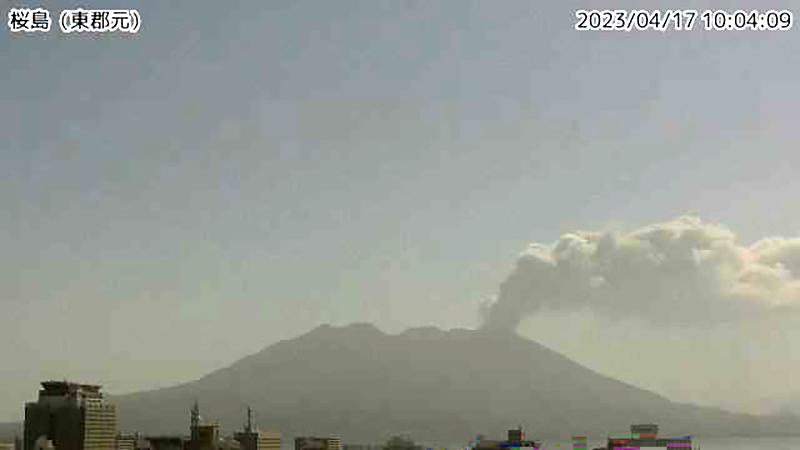
Two eruption events were reported in the Minamidake summit crater during April, neither of which were explosions; no eruptions occurred at the Showa crater. Eruption plumes rose 1.5 km above the crater rim and nighttime crater incandescence persisted nightly at the Minamidake crater. The number of volcanic earthquakes deceased to 38 and according to the Kagoshima Local Meteorological Observatory, a total of 3 g/m2 of ash fell over a period of four days during the month. The amount of sulfur dioxide released during the month ranged 1,800-2,700 t/d. An eruption event at 0955 on 17 April generated an eruption plume that rose 1.5 km above the crater rim (figure 145).
Eruptive activity during May consisted of 17 eruptions, 10 of which were explosion events. Volcanic plumes rose 2.3 km above the crater rim and large ejecta traveled 800-1,100 m from the Minamidake summit crater. Activity at the Showa crater was characterized by 11 eruption events and material was ejected 300-500 m from the crater. Nighttime crater incandescence was observed at both summit craters. The number of monthly volcanic earthquakes increased to 88 and the amount of ashfall recorded was 10 g/m2 over a period of 13 days during the month. According to a field survey, the amount of sulfur dioxide released ranged 1,800-3,900 t/d.
Explosions were recorded at 0422 on 2 May, at 0241 and at 1025 on 3 May, at 1315 on 9 May, at 2027 on 17 May, at 0610 on 24 May, at 1327 on 25 May, at 0647 and 1441 on 26 May, and at 1520 on 28 May. Resulting eruption plumes rose 400-1,800 m above the Minamidake crater and drifted SW, W, and N. On 14 May an eruption plume was visible above the Showa crater at 0859 that rose 1.7 km above the crater rim (figure 146). An eruption event at the Minamidake summit crater occurred at 1327 on 25 May; the eruption plume rose 2.3 km above the crater rim (figure 147).
JMA reported four eruptions occurred during June, two of which were explosion events. Eruption plumes rose as high as 2.5 km above the Minamidake crater rim and large volcanic blocks were ejected 500-700 m from the crater rim. At the Showa crater, seven eruptions occurred, one of which was an explosion event. Eruption plumes rose 1.5 km above the Showa crater rim and large material was ejected 500 m from the crater rim. Nighttime incandescence was reported for both summit craters. There were 73 volcanic earthquakes detected during the month and a total of 3 g/m2 of ashfall during eight days of the month. According to a field survey, the amount of sulfur dioxide emissions released ranged 1,400-1,900 t/d. On 5 June at 0012 an explosion generated an eruption plume that rose 400-1,000 m above the Minamidake crater and drifted SE. An explosion at the Minamidake crater occurred at 1401 on 7 June that generated an eruption plume that rose 2.5 km above the crater and drifted SE (figure 148). A single explosion was reported at the Showa crater at 0438 on 22 June. The eruption plume rose 600 m above the crater rim and large blocks were ejected 500 m from the crater rim. This is the first report of an explosion at the Showa crater since October 2017, according to JMA.
Geological Summary. The Aira caldera in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay contains the post-caldera Sakurajima volcano, one of Japan's most active. Eruption of the voluminous Ito pyroclastic flow accompanied formation of the 17 x 23 km caldera about 22,000 years ago. The smaller Wakamiko caldera was formed during the early Holocene in the NE corner of the caldera, along with several post-caldera cones. The construction of Sakurajima began about 13,000 years ago on the southern rim and built an island that was joined to the Osumi Peninsula during the major explosive and effusive eruption of 1914. Activity at the Kitadake summit cone ended about 4,850 years ago, after which eruptions took place at Minamidake. Frequent eruptions since the 8th century have deposited ash on the city of Kagoshima, located across Kagoshima Bay only 8 km from the summit. The largest recorded eruption took place during 1471-76.
Information Contacts: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/indexe.html); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).