Report on Ketoi (Russia) — 7 August-13 August 2013
Smithsonian Institution / US Geological Survey
Weekly Volcanic Activity Report, 7 August-13 August 2013
Managing Editor: Sally Sennert.
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2013. Report on Ketoi (Russia) (Sennert, S, ed.). Weekly Volcanic Activity Report, 7 August-13 August 2013. Smithsonian Institution and US Geological Survey.
Ketoi
Russia
47.35°N, 152.475°E; summit elev. 1172 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
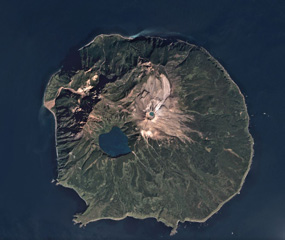
SVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Ketoi's Pallas Peak was detected in satellite images during 5-7 and 9 August, and possibly during 10-11 August. Steam-and-gas emissions were detected on 9 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Yellow.
Geological Summary. The circular 10-km-wide Ketoi island, which rises across the 19-km-wide Diana Strait from Simushir Island, hosts of one of the most complex volcanic structures of the Kuril Islands. The rim of a 5-km-wide Pleistocene caldera is exposed only on the NE side. A younger stratovolcano forming the NW part of the island is cut by a horst-and-graben structure containing two solfatara fields. A 1.5-km-wide freshwater lake fills an explosion crater in the center of the island. Pallas Peak, a large andesitic cone in the NE part of the caldera, is truncated by a 550-m-wide crater containing a brilliantly colored turquoise crater lake. Lava flows from Pallas Peak overtop the caldera rim and descend nearly 5 km to the SE coast. The first historical eruption of Pallas Peak, during 1843-46, was its largest.